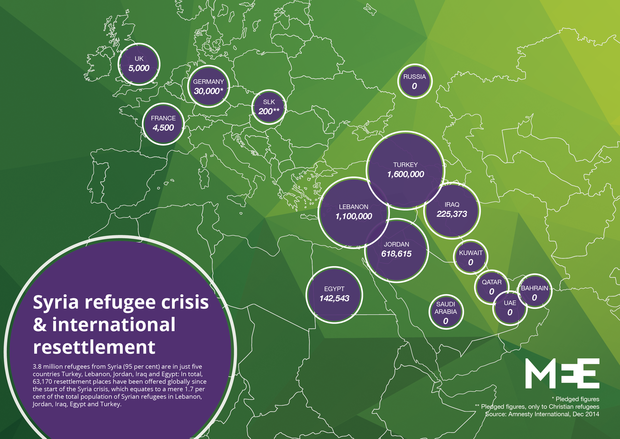
There are many ways you can look at things happening in Syria. Here we’re sharing views of 3 Quora writers who’ve written great answers to this question and they’ll definitely help you understand the conflict in a better way.
View 1: Culmination of multiple events starting from 2003
What is happening in Syria has a lot to do with what happened in Iraq and is a culmination of a lot of events starting from the US invasion of Iraq in 2003. The below points will put forward my arguments supported by references/sources.
- In the year 2003, the United States decided to invade Iraq, after building a huge world public opinion regarding the presence of WMDs(weapons of mass destruction) in Iraq. The US forces reached Baghdad in two months, and the invasion was complete, but the war was just getting started. Insurgency in Iraq picked up, the regular troops of the Iraqi army, who were still very loyal to Saddam Hussain, started engaging the Americans in firefights in various cities across Iraq.
Reference(s): 2003 invasion of Iraq
- Due to this insurgency, which started just after the invasion of Iraq, many US soldiers got killed. This peaked from 2003 to 2006, and during this period there was an extensive radicalization of particularly the Islamic Sunni insurgents, who were now no longer the regular troops of the Iraqi army, but Mujahideens(Islamic “holy” warriors) ready to wage armed Jihad against the west and also against the Shia minorities in the surrounding areas.
- From 2006 to 2008, Iraq underwent a bloody sectarian civil war, scores of Shias were killed by the Sunnis, and in retaliation some Sunnis were also killed. The main casualty of this civil war were Shias. Al-Baghdadi (the present ISIS chief) had then formed a group called the IS(Islamic State), which was responsible for scores of bombings mainly targeting the Shia community. As a result more than 4 million Iraqis became refugees.
Reference(s): Iraqi insurgency (2003–11),
Iraq violence: Car bomb kills scores in mainly Shia town – BBC News
- Now, a third wave of insurgency hit Iraq, this spanned from 2008 to 2011, like the previous insurgencies, this was a mix of sectarian violence and waging armed jihad against the US troops. In the December of 2011, the US forces had completely withdrawn from Iraq, leaving Iraq in a state of absolute and complete anarchy. Though the US said that they had left Iraq in the able hands of the new “democratic” Iraqi PM Nouri al-Maliki, but i think that it was a huge BLUNDER on part of president Obama to order complete withdrawal of US troops from Iraq in the December of 2011.
Ref: Withdrawal of U.S. troops from Iraq
- The insurgency in Iraq continued even after US withdrawal, and to put it bluntly, Iraqi PM Nouri al-Maliki failed terribly to contain it even after outside US support. The people of Iraq, generally the Sunnis felt alienated by Maliki because Maliki discriminated against the Sunnis and he mainly had a Shia dominated government. Maliki even gave more preference to Shias than Sunnis in the Iraqi army. This further alienated the Sunnis from the newly American blessed Iraqi govt. To put it simply, Maliki failed to have a inclusive govt that would have taken care of the welfare of both Sunnis and Shias. This was the main reason why many of the Sunni dominated areas got controlled and radicalized by people like Al-Baghdadi. By 2014, Al-Baghdadi led ISIS(Islamic state of Iraq and Syria) controlled majority of the Sunni areas of Iraq.
Refs: Iraqi insurgency (2011–14)
How Iraq unraveled since the U.S. withdrawal, in 10 steps
- On 29 June 2014, ISIS announced the establishment of a worldwide caliphate. Al-Baghdadi was named its caliph. Systematically, after 2011 the effects of the Arab spring(rebellion in the Arab world against their rulers) started overflowing into Syria.
I, personally, DO NOT think that the Arab spring was a people’s movement, rather it was a extension of the US foreign policy to have more control over the middle east by placing leaders in power who will show loyalty only to the United States. Thus, the US wanted to establish client states in the middle east, for many reason, and one being access to huge oil reserves. I know, many people will have contrary view points, but i have stated what i think, according to me, what i have stated is a writing on the wall, if you look closely to what has happened in the middle since 2003.
- The Arab spring led to a lot of protests against the Assad govt. But when they realized that Assad is not relenting, a fraction of the Syrian army broke off and formed the free Syrian army with the help of the US. The rebels/free Syrian army holds territory in the north-western part of Syria. From 2011 to 2014, the ISIS started occupying large areas, mainly Sunni dominated areas, of Iraq and Syria. During the Syrian civil war, the ISIS captured the Syrian city of Al-Raqqah, which became its headquarters in Syria.
Refs: Al-Raqqah
Pictorial Representations:
In the above pic, the red area is the area that is infested by ISIS militants. You can see how it expanded from Iraq to Syria.
In the above pic, only the Syrian map is shown, here you can see the areas controlled by both ISIS/ISIL and the rebels(“Free” Syrian Army).
- Now, to put it in a nutshell, there are four major players in Syria today:
- The Russians forces, led by Vladimir Putin.
- The Syrian Army, led by President Assad of Syria.(Supported By The Russians).
- ISIS led by Al-Baghdadi. (According to me, secretly backed by the US to destabilize the Assad govt)
- The Free Syrian Army, supported/backed by the US.
- The United States and its Allies.
-
Above pic shows the air strike done by Russians and the US on various locations in Syria.
- On 30th September 2015, the Russians started carrying out air strikes against both the rebels and ISIS, because Putin is SICK and TIRED of american imperialistic ambitions and a bad habit of interfering in other nations and toppling governments in the name of freedom and democracy, only to establish a client subservient state towards the US. I think this was a bold decision by Putin, even after Russian is reeling under imposed sanctions.
Ref: Russian military intervention in the Syrian Civil War
- As the above nine points depict, the Syrian situation is a complex situation. The Russians have gone in hard, and i will not shy away from saying that i am backing the Russians on this. This entire situation has occurred because of american imperialistic ambition of toppling governments. The US should realize that there are no “good” or bad terrorist, terrorist are just terrorists. The “free” Syrian army and ISIS are almost fighting like allies in this war backed by the US, they are receiving arms and full support of the US. More than anybody else, the people of Syria have suffered, and i sincerely hope the Russians are able to set the record straight and bring peace to the area.
By: Raveesh Kanwal on Quora
Read Kaveesh Kanwal‘s answer to What is happening in Syria? on Quora
View 2: It’s a proxy war between Iran and Saudia Arabia
The Syrian war is a complex conflict, in order to understand it, you need to have a good overview of every groups involved. If the war started by some socials and political revendication, now This war is mainly a proxy war between Iran and Saudia Arabia. If you don’t understand this, you can’t get any clue why all these people are fighting for. Many vassals/allys are involved too so it’s why I’m gonna start by presenting every force in the Battlefield :
Iran :
commander : Ali Khamenei
who : Iran is a long time enemy of the Saudi and many arabs because of thousands reasons mainly cultural, historical and geopolitical. Get this in your head, Iran hates Saudi and Saudi hates Persian. Saudians even ask the Americans to attack them. In the past, Iran was also an Irak ennemy but since the fall of saddam, they have managed to secure one part of this country as an ally and to put the USA (another enemy) into a deadly and expensive war.
why : El-Assad is one of the few ally that Iran have. Since Ahmadinhejab, Iran is very isolated both in diplomatic and economics field. If Syria fall, the next target is obviously Iran. It’s why Iran is sending a lot of weapons,, “volunteers” and technical advisors for El-Assad.
bonus : El-Assad is an alaoui (a branch of the shiism) so are the Iranians
Syria :
commander :
who : Until the accidental death of his brother, Bachar was not involved in politics nor in army. In 2000, when his father die, he took control of the government, the army and the Baath party (only allowed). Many thought that he would be more soft than his father since he lived a long time in England.
why : In the wake of the arab Spring and the shameful fall of Ben Ali, Bachar choose an hard line to repress the mass protestations. After very tough starts, he have been able to keep fighting thanks to massive Iranian help.
Hezbollah :
commander : Hassan Nasrallah
who : The Hezbollah (meaning the party of God) has been created after the Lebanon war of 1982. Like the other shi’a group, Hezbollah has always been backed by the Iranian who use them to fight the Israelien sometimes successfully like in 2006. Hezbollah is powerful and well organized.
why : Nasrallah have stated : “If Syria falls into the hand of America, Israel and takfiris, the resistance (Hezbollah) will be besieged and Israel will enter Lebanon and impose its will.” Therefore, the immediate interest of the Hezbullah is to keep a friendly state in Syria and Iran because if they fall, Hezbullah will be soon defeated.
Iraq :
commander : Moqtada Al Sadr
who : Al Sadr is a son of an prominent shia ayatollah killed by Saddam. During the second Iraq war, he led the resistance against the USA. His partisans are essentially based in the south of the Iraq around the city of Nadjaf or Bassorah. He is an ally of Iran.
why : Officially, the Mahdi Army is in Syria to protect a famous shrine near Damas. In fact, many see Al Sadr as a puppet of the Iran and they want to fights iraqi sunnis too.
Russia :
commander : Vladimir Putin
who : USSR then Russia have backed Arab Socialist oriented nations since the 50’s like Egypt, Syria, Yemen etc
why : Russia got in Syria an harbour in warm water at Tartus. Let’s talk wikipedia : Tartus is the last Russian military base outside the former Soviet Union, and its only Mediterranean fueling spot, sparing Russia’s warships the trip back to their Black Sea bases through straits in Turkey, a NATO member. Plus, Syria always bought weapons from USSR/Russia. Russia is also a small support of the Iranians mainly because they are opposed to the USA.
Now let’s see the Saudi side.
Syrian rebels also knows as National Coalition for Syrian Revolutionary and Opposition Forces or Free Syrian Army:
commander : Salim Idriss
who : a coalition of various forces opposed to Bashar. There is a lot of civilian harmed by El-Assad, many sunni who lost everything but overall many military who fled Bashar Army for various reasons. Shortly after the begining of the revolution, the FSA start their operations.
why : FSA stated that their only goal is to remove Assad from power. They operate in the whole country (countryside include) and led thousands attacks against loyal forces. They are the secular part of the rebellion. FSA is backed by France, Uk, Europe, USA, Turkey, Saudia Arabia and recognized by many countries.
Saudi Arabia :
commander : Abdullah of Saudi Arabia
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wiki…
who : The Saudians and various emirates of the Gulf like Qatar are involved with the rebels
why :
The Saudians are like i have said a long time enemy of the Iranians. They are involved in this war by funding heavily the islamist rebels and organizing the diplomatic support.
Al-Nusra Front a.k.a Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
commander : Abu Mohammad al-Golani
who : Al-Nusra is an army of sunnite djihadist listed as terrorist by the UNO why arabs (algerians, egyptians, palestinians, jordanians, saudians) and others country like the Tchetchens or the Algerians. They are affiliated to Al Qaeda and are describing themselves like an extension of Al Qaeda Iraq.
why : El Assad were the enemy of sunnites islamist like all the other “socialist” leaders (Nasser, Khadafi, Ben Ali etc).Al Nusra is heavily backed by the Turkish and the Qatar.
USA and his occidentals vassal
commander : Barack Obama
who : USA are enemy of the Iran since 1979 plus they are one of the close ally of Saudians and Israeliens
why : Due to excessive political and economical pressure, USA can’t afford to intervene directly (like in Libya) but they support the rebels by isolating El Assad. They have started to provide some light weaponry and intelligence
Israel :
commander : Benjamin Netanyahu
who : Israel is a enemy of Syria since 1948. They are occupying the Golan Heights (which is part of Syria). Syria is also one of the main support of the Hezbollah who are one of the deadliest enemy of Israel.
how : Israel want to weaken Syria position which was quite strong. They have bombed some Syrian plants, factory and AA sites.
Turkey
commander : Recep Tayip Erdogan
who : Syria and Turkey always had complex relations. Once part of the ottoman empire, Syria have alterned with turkey various years of warm and cold. While El Assad father was president, relations were really cold because Syria was in the Soviet influence (while Turkey in the USA side). Turkey have constructed a lot of dam to keep all the Euphrates and Tigris water. On the other side, El Assad have support the PKK (who were the worst enemy of the turkish). Before the syrian uprising, the relationship were a bit more warm.
why : Erdogan was seeing himself like a model for the muslim world but when he have see the Kurdish uprising being successful in the northern part of Syria, he choose to intervene massively by providing heavy support for Islamist rebels (hospital, money, tanks, artillery, weapons, intelligence).
There is third party involved, the Kurdish who are trying to liberate themselves from decades of arab repression.
YPG : People’s Protection Units
commander :
Salih Muslim Muhammad
who : YPG are the armed forces of the Kurdish uprising in Syria. It’s mainly a militia (even if they are thousands and thousands) backed by PKK. They have several strongholds in the northern parts of the country where the Kurdish are the majority
why : Kurdish have faced a long time oppression where almost any rights have been denied. They are supposed to be 3 millions. They try to follow the same way of the Kurdish of Iraq (independance de facto). They face everyday heavy islamist assault.
PKK :
commander : Murat Karayılan
who : once a marxist-leninist party based in Turkey, PKK is a party very powerful, deeply rooted in every parts of Kurdistan and in the Kurdish diaspora.After decades of bloody gerilla against the Turkish army, PKK is now seeking a political solution.
why : once an ally of El-assad (Ocalan, the historical leader was during years in the Bekaa), PKK is trying to get the opportunity of an autonomy for the Kurdish in Syria. They have proclaim a cease fire with the Turks and they are moving their units in Syria
KDP : Kurdistan Democratic Party
commander : Massoud Barzani
who : son of the legendary Kurdish fighter Mustafa Barzani, Barzani is actually the most powerful kurdish leader. He leads the independant (de facto but not officially) Kurdish Regional Government in Iraq. Thanks to the oil, the KDP is rich and very powerful (dozens of thousands fighters very well equiped)
why : As a prominent leader, Barzani try to unify under his control all Kurdish parts but he got actually some good relations with Turkey and USA.
By : Martin Dupont
Read Martin Dupont‘s answer to What is happening in Syria? on Quora
View 3: Rich people trying to get even richer
Here’s probably the shortest and simplest explanation of why the whole Syria thing happened, and what’s behind all of it:
So there’s this big ass oil and gas field that’s half in Qatar and half in Iran.
Qatar wanted to make some money from it, so Qatar along with Saudi Arabia decided to make a natural gas pipeline from Qatar to Europe, which was going to pass through Syria.
They have asked Assad to give them permission to build it, but he said a big fat NO.
Later, Iran wanted to make a pipeline which would be passing through Syria, and Assad said YES.
This has made Qatar, Saudi Arabia and by extension USA very angry, since they also have a massive interest in making sure this fuel from Qatar goes to Europe.
As a result, they all threatened Assad, and the whole revolution thing was set in motion, by labeling Assad as a mad dictator, pointing all mass media to him, and deciding to “bring some freedom to his country” because he apparently “started murdering his own people” and so on and so forth. Even though most Syrians support Assad.
Now you might ask – “Why is Russia helping Syria?”
Well, because every European knows that Europe is buying its gas from Russia, so building a pipeline from Qatar to Europe would drastically affect the Russian economy, and enrich Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and the US – making sure the petrodollar stays strong.
Billions of dollars have been invested into this revolution; from spreading propaganda through mass media, to using Islam as a weapon and supplying extremists with arms.
Who has to profit the most if Assad falls? Saudi Arabia, Qatar, USA – all because of oil and gas.
Who has to profit the most if Assad remains? Syria, Russia – all because of oil and gas.
Ultimately, it’s completely up to Syria as a sovereign nation to choose who they do business with. But some people don’t like or respect that, and want things their way, so they want to remove the current government and put someone else in place. Someone who shares their views and profits.
And can you now deduce who started it all, and why?
That’s right. But Syria and Russia still get all the hate pointed towards them through mass media. And it’s easy to hate Russians now, what with the whole Ukraine fiasco still fresh in everyone’s minds.
In the end, it’s all about greed and money for a select few incredibly rich groups to become even richer. Someone’s going to utilize that oil and gas field eventually, and they’ll make hundreds of billions, if not trillions.
Everyone’s trying to make sure it’s them, and not the other side.
But who suffers the most because of this? Your average everyday people, while rich men fill their pockets with more money.
Quite a sad state of affairs, if you ask me.
While certain people will profit from this fossil fuel field, all it does now is just breed incredible hate in ordinary people of all the countries involved who don’t have a stake in any of it – pitting them against each other because they blindly believe that their country is always in the right no matter what.
I’m as neutral as you can get in any of this, and carefully research both sides of the conflict since I’m fluent in these languages. Don’t hate.
I usually keep my political opinions to myself – but there’s just too much misinformation going on regarding Syria.
Also, this bullshit can easily escalate into WW3, given enough trigger happy idiots who blindly follow orders.
It’s funny how we’re lead to believe that Assad is the dumbest idiot dictator on the planet, because he invited UN inspectors to come to his country – and on the very day that he brought them in, he somehow decides to attack and bomb HIS OWN PEOPLE, 10 miles away from where the inspectors arrive.
Seems legit.
Ex-Marine Goes Crazy, Blows Whistle On Syrian False Flag and Real Agenda
By: Andrius Saulis
Read Andrius Saulis‘ answer to What is happening in Syria? on Quora